DbView Database visualization
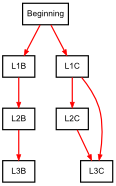
A join is associated to a foreign key. It represents a relation between two fields : The "reference" field and the "dependent" field.
- The dependent field is the field that declares the foreign key (which can be hard or soft).
- The reference field is a field to which the dependent field is associated.
We could say that: The value of the dependent field depends on the value of its associated reference (field).
A join is associated to cardinalities.
Graphically, a join is represented by an arrow with a 4-column grid in the middle of it. The start of the arrow is the dependent table. The end of the arrow is the reference table.
dbview.sh export -exporter dot-full -zoom sfk_dependent,sfk_reference -db-daptor mysql -host localhost -user root -password root -dbname mydb -port 8889 -fkmatcher fk-us-target-table-name -layout v > graph.dot
dot -Tgif -Ograph graph.dot
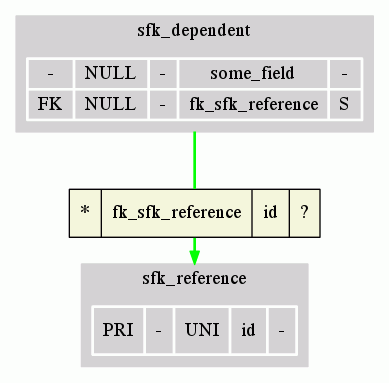
dbview.sh export -exporter dot-full -zoom hfk_dependent,hfk_reference -db-daptor mysql -host localhost -user root -password root -dbname mydb -port 8889 -fkmatcher fk-us-target-table-name -layout v > graph.dot
dot -Tgif -Ograph graph.dot
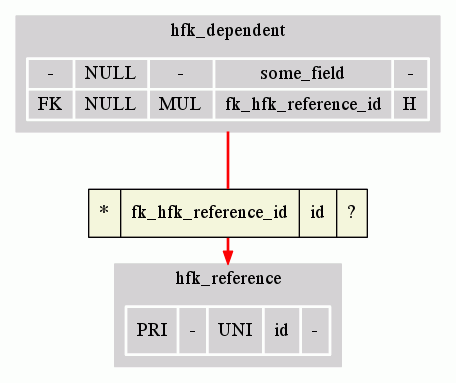
Starting from the left column of the join's grid, we find:
- The cardinality of the association between one dependent record and some reference records (see cardinalities).
- The name of the dependent field, in the dependent table.
- The name of the reference field, in the reference table.
- The cardinality of the association between one reference record and some dependent records (see cardinalities).